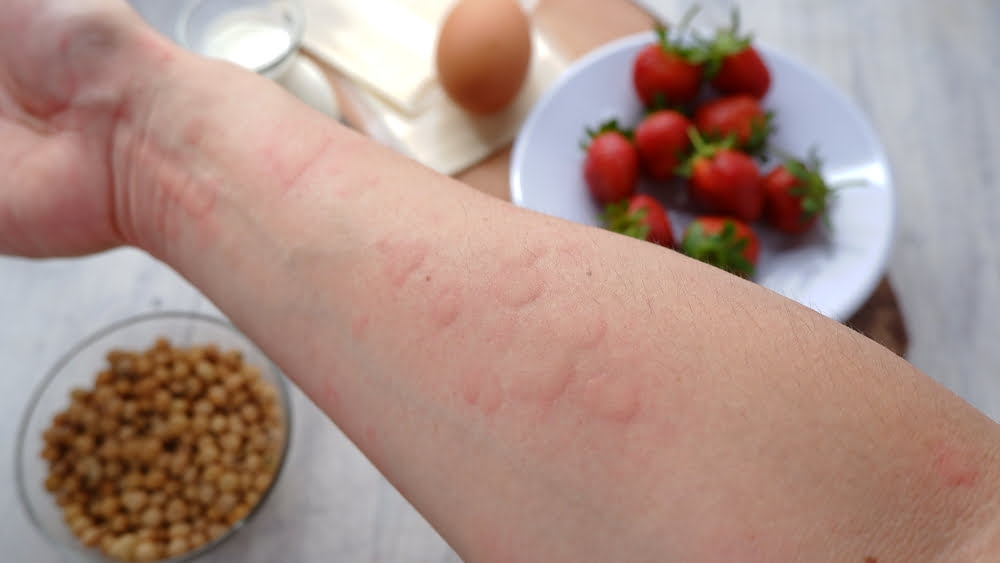
Did you know that something as small as a peanut can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction in some people? Or that an asthma attack can be triggered just by eating a spoonful of mushrooms? Even something as simple as black pepper can cause a severe migraine for certain individuals. These may sound unusual, but they are very real experiences for those with food allergies.
What is a Food Allergy?
A food allergy is an immediate reaction from the immune system after eating a specific food. If someone has a food allergy, their immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless protein in the food as a threat and overreacts to it. Even a small amount of the allergenic food can cause symptoms. In some cases, these symptoms can be severe and even life-threatening, such as anaphylaxis, which involves swelling of the throat, narrowing of the airways, and difficulty breathing. Anaphylaxis can affect multiple parts of the body at once, causing symptoms like stomach pain and a rash simultaneously.
It’s important to note that food allergies are different from food intolerances. Food intolerance does not involve the immune system and typically results in less severe symptoms. For example, lactose intolerance occurs when a person lacks the enzyme needed to digest lactose, the sugar in milk, leading to gas, bloating, and abdominal pain after consuming dairy products.
Common Food Allergens
While people can be allergic to any food, some allergens are more common than others. In fact, eight foods are responsible for 90% of all food allergic reactions: milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts (like walnuts and cashews), fish, shellfish, soy, and wheat.
Homeopathic Treatment for Food Allergies
Homeopathy offers a natural way to manage food allergies by helping to balance and optimize the immune system. Unlike conventional treatments that only address the symptoms, homeopathy aims to correct the underlying imbalance that causes the allergy. By choosing the right homeopathic remedy, individuals can find relief from specific food sensitivities or intolerances.
Here are some effective homeopathic treatments for common food allergies:
- Calcarea Carb for Milk Allergy: This remedy is beneficial for those who experience vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea after consuming milk products. It is also helpful if there is a cold sensation in the abdomen.Usage: For symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and loose stools after consuming milk, Calcarea Carb in low potency (30C) can be taken 2-3 times a day. If symptoms persist, a higher potency (200C) may be taken once a day, but it’s best to consult with a homeopath before using high-potency remedies.
- Colchicum for Egg Allergy: Colchicum is recommended for gastrointestinal symptoms that occur after eating eggs, such as abdominal bloating, gas, and painful cramps.Usage: If there is stomach pain or pressure, especially with gas, Colchicum 30C can be taken 2-3 times a day. For more persistent symptoms, consult a homeopath before taking a higher potency.
- Urtica Urens for Shellfish/Fish Allergy: This remedy is effective for skin reactions like intense itching, burning, and hives after consuming shellfish or fish.Usage: For skin rashes or hives, Urtica Urens 30C can be taken 2-3 times a day. Higher potencies should only be used under the guidance of a professional.
- Lycopodium for Wheat Allergy: Lycopodium is useful for managing digestive issues like bloating, heartburn, and gas that occur after consuming wheat products.Usage: For symptoms like bloating and acid reflux after eating wheat, Lycopodium 30C can be taken 2-3 times daily. Higher doses should be taken with caution and under professional supervision.
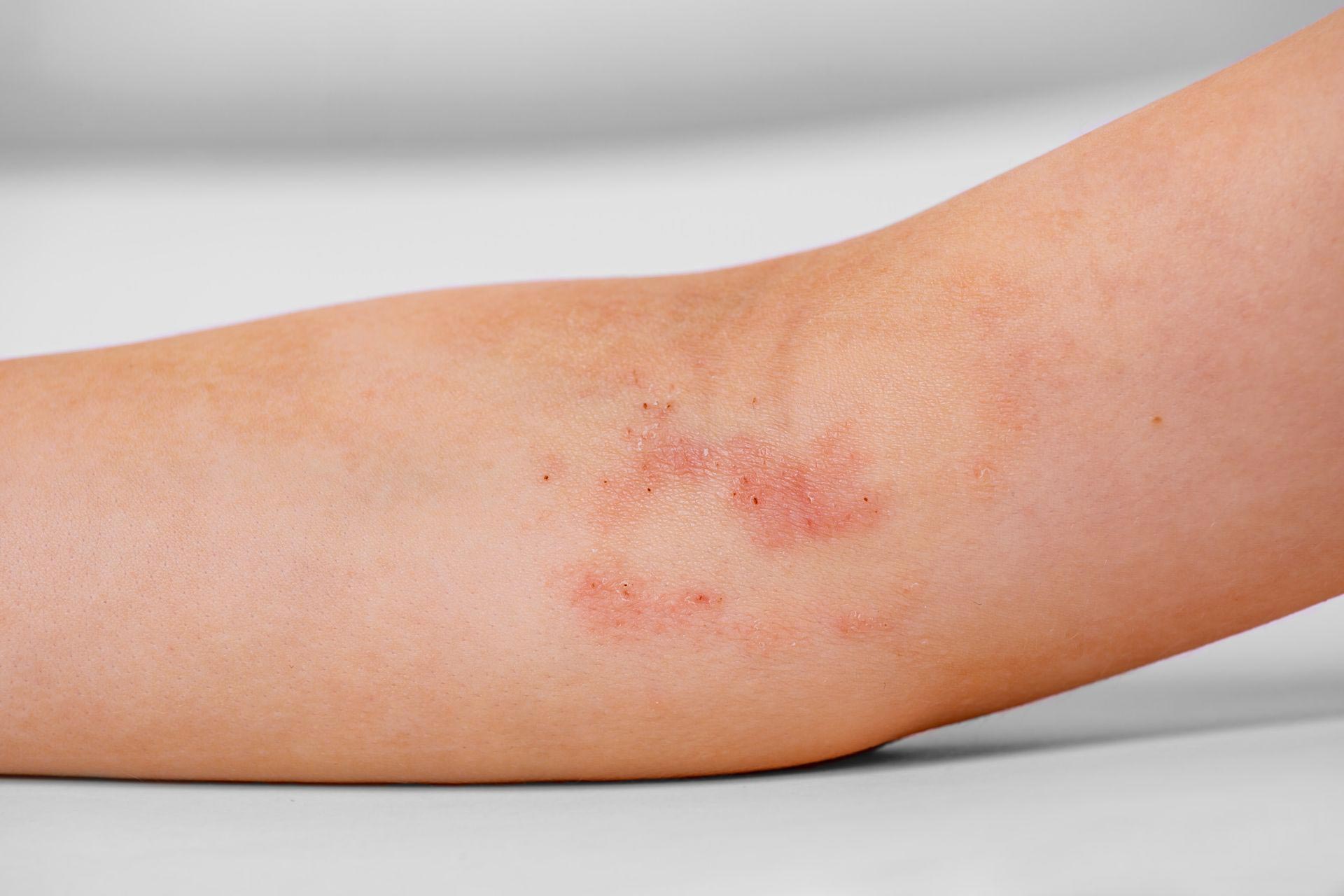
- Apis Mellifica for Skin Reactions in Food Allergies: Apis Mellifica is ideal for treating hives and other skin issues related to food allergies. It is especially helpful for severe itching, burning, and stinging sensations.Usage: For skin reactions like hives or swelling, Apis Mellifica 30C can be used 2-3 times a day. Higher potencies should only be used with professional guidance.
Understanding Different Types of Food Allergies
- Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome (Oral Allergy Syndrome): This occurs when people with hay fever react to proteins in certain fruits, vegetables, nuts, and spices that are similar to pollen proteins. Symptoms usually include itching in the mouth, and in severe cases, throat swelling or anaphylaxis.
- Exercise-Induced Food Allergy Syndrome: This happens when consuming certain foods before exercise leads to allergic reactions like hives or even anaphylaxis, especially when the body temperature rises.
- Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES): A severe condition that causes vomiting and diarrhea hours after consuming a trigger food, like milk or soy. It is most common in infants.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis: This condition involves inflammation of the esophagus due to a reaction to specific food proteins and is often seen in people with other allergic conditions.
Symptoms of Food Allergies
Food allergy symptoms can range from mild to severe and often appear within minutes to two hours after eating the allergen. Common symptoms include:
- Itching in the mouth
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain
- Hives, eczema, or swelling
- Difficulty breathing, wheezing, or repetitive cough
- Shock or a drop in blood pressure
- Tight throat or trouble swallowing
- Dizziness or fainting
In rare cases, symptoms may be delayed and occur four to six hours after exposure, such as in children who develop eczema as a reaction to certain foods or individuals allergic to red meat after a tick bite.
How Food Allergies Work
When a person with a food allergy consumes an allergen, their immune system produces antibodies called IgE. These antibodies attach to mast cells, which are found throughout the body, especially in the digestive tract, nose, throat, and lungs. When the allergen is consumed again, it binds to the IgE on the mast cells, triggering the release of histamine and other chemicals. This release causes allergic symptoms, which can vary depending on where the histamine is released in the body.
Risk Factors for Food Allergies
- Family History: A higher risk exists if there is a family history of allergies, asthma, or eczema.
- Age: Children, especially infants, are more susceptible to food allergies. Many outgrow their allergies as their digestive system matures.
- Asthma: Those with asthma may experience more severe allergic reactions.
- Other Allergies: Individuals with one type of allergy are more likely to develop others.