Knee Arthritis: Understanding and Treating the Condition
Knee arthritis is a condition characterized by inflammation in the knee joints. This inflammation can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, swelling, stiffness, tenderness (pain when touching the affected area), and cracking or popping sounds when moving the knee. The range of motion in the knee joint can also become limited, and in severe cases, the knee may even become deformed.
Homeopathic Treatment for Knee Arthritis
Homeopathy offers a promising approach to managing knee arthritis. It focuses on alleviating symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and swelling while also reducing inflammation and preventing further joint damage. This holistic approach can effectively address both acute and chronic cases of knee arthritis. If treatment is started early, it may even lead to a complete recovery in mild to moderate cases, depending on the underlying cause. In more severe cases, while homeopathy may not reverse the damage already done, it can still help manage symptoms and can be used alongside conventional medicine without interfering with its effects.
Homeopathy treats knee arthritis by targeting its root cause, which can vary from person to person. Whether arthritis stems from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, injury, gout, or another cause, homeopathic remedies work deeply to address the underlying issues, providing substantial relief.
These natural remedies are safe and have no side effects, unlike conventional treatments, which often involve painkillers, NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), corticosteroids, or DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs). These conventional medications typically offer only temporary relief, can lead to dependency, and may cause various side effects. In contrast, homeopathic treatments offer long-lasting relief without creating dependency.
Homeopathic medicines are chosen specifically for each individual after a thorough assessment of their symptoms and overall health. Therefore, it is essential to consult a qualified homeopathic physician before starting any homeopathic treatment for knee arthritis. Self-medication is not recommended, as the choice of remedy, its potency, dosage, and frequency can vary greatly from case to case.
Top 7 Homeopathic Medicines for Knee Arthritis
- Rhus Tox: This is often the first choice for managing knee arthritis, particularly when the pain worsens during rest and improves with movement. It is effective in relieving pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee and helps improve mobility.
- How to Use: Typically taken in 30C potency three to four times a day, depending on the pain’s intensity.
- Bryonia Alba: This remedy is ideal for knee pain that is aggravated by movement and alleviated by rest. It is especially useful for those who experience sharp, stabbing pain while walking.
- How to Use: Often used in 30C potency two to three times a day.
- Apis Mellifica: This medicine is particularly helpful for knee arthritis accompanied by significant swelling and stinging or shooting pain.
- How to Use: Start with 30C potency twice or thrice a day and reduce the dosage as symptoms improve.
- Benzoic Acid: Effective for knee arthritis associated with high uric acid levels, such as gout. It helps manage pain, swelling, and cracking sounds in the knee.
- How to Use: Usually recommended in 30C potency two to three times a day.
- Osteo-Arthritic-Nosode: This remedy, made from the synovial fluid of an osteoarthritic knee, is specific for treating osteoarthritis of the knee. It helps relieve pain, stiffness, and swelling and improves joint mobility.
- How to Use: Typically taken in 200C potency once a week. Do not exceed this dose without consulting a physician.
- Arnica Montana: This remedy is excellent for knee arthritis resulting from an injury. It helps reduce swelling and pain and promotes healing in the affected areas.
- How to Use: Generally used in 30C potency three to four times a day, based on the pain’s intensity.
- Ledum Pal: Best suited for knee pain accompanied by cracking sounds during movement, along with swelling, stiffness, and weakness in the knees.
- How to Use: Usually taken twice a day in 30C potency. Higher potencies can be used under the guidance of a homeopathic physician.
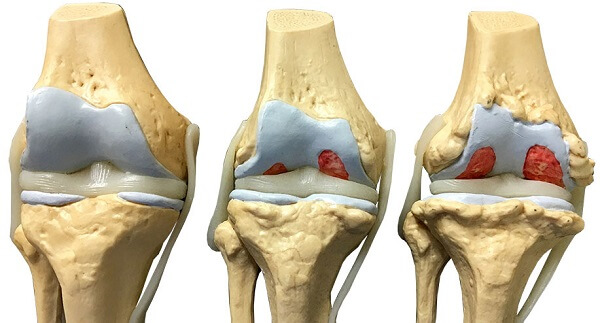
Causes and Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Understanding the structure of the knee joint can help explain the causes and symptoms of knee arthritis. The knee is a complex joint made up of bones, cartilage, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and other components. Arthritis can affect any of these parts, leading to various symptoms.
Common Causes of Knee Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis, especially in older adults, where the cartilage that cushions the knee joint gradually wears away, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
- Symptoms: Deep pain in the knee, especially after exercise or weight-bearing activities, joint stiffness after periods of inactivity, cracking or grating sounds, and, in advanced cases, pain even at rest.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue, causing pain, swelling, and joint deformity.
- Symptoms: Knee pain and swelling, stiffness that is worse in the morning or after inactivity, heat and tenderness in the joint.
- Gout: A type of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid, leading to the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints, which causes inflammation and pain.
- Symptoms: Intense knee pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness.
- Injuries (Post-Traumatic Arthritis): Arthritis that develops after an injury to the knee joint, such as a ligament tear, meniscus tear, or broken bone. This type of arthritis can lead to joint instability and degeneration over time.
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, and reduced joint function following an injury.
Diagnosis of Knee Arthritis
To diagnose knee arthritis, doctors usually start with an X-ray to look for changes in the bones and joint space. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess inflammation levels (such as ESR and CRP) or to check for specific markers associated with rheumatoid arthritis (like rheumatoid factor and Anti-CCP antibodies). In cases where gout is suspected, uric acid levels are measured. Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI or CT scans, may be used to examine soft tissue damage in the joint more closely.